FAQ: Melanoma
- What is melanoma?
- Is melanoma a serious disease?
- What causes melanoma?
- What does malignant melanoma look like?
- Can melanoma be cured?
- Can melanoma be prevented?
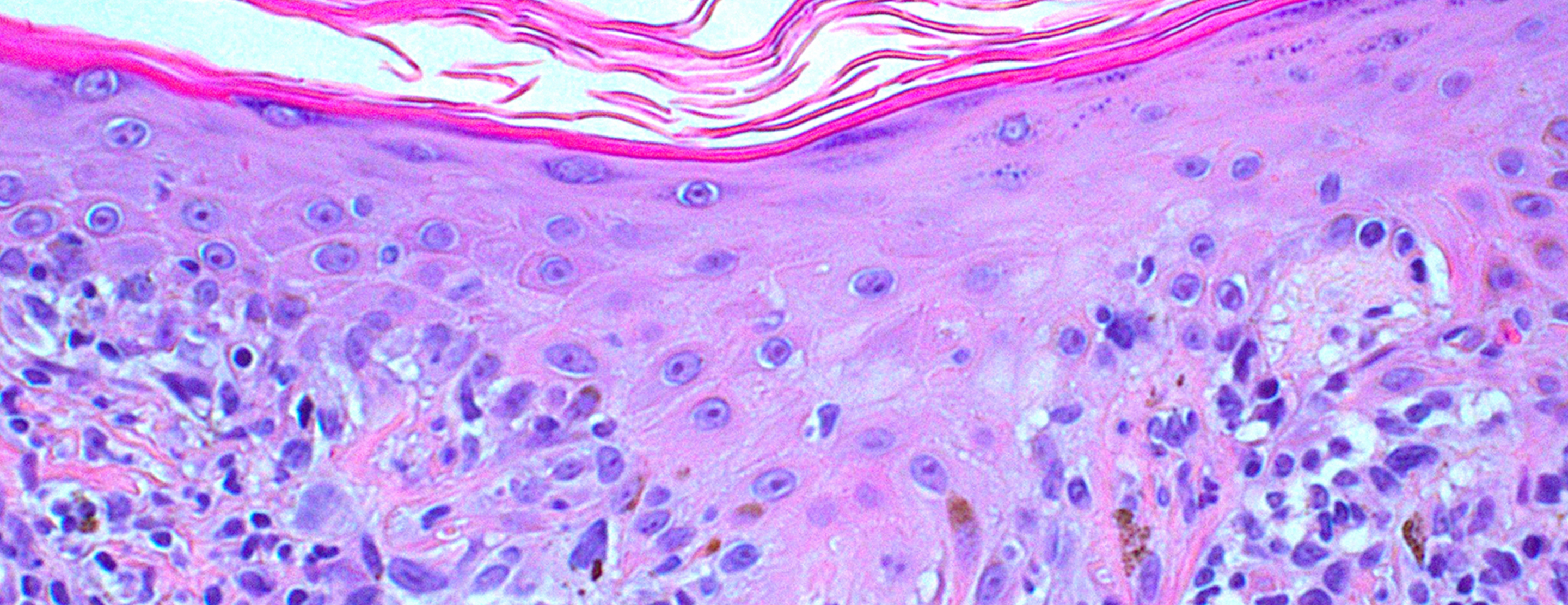
Melanoma is a very serious skin cancer characterized by the uncontrolled growth of cells that produce pigment, the substance in skin that produces color. Melanomas may appear suddenly and without warning. They are found most frequently on the face and neck, upper back and legs, but can occur anywhere on the body.
Is melanoma a serious disease?
Yes. In later stages, malignant melanoma spreads to other organs and may result in death. If detected in its early stages, melanoma can be treated successfully.
Excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation of the sun is the most common cause of melanoma. Other possible causes include genetic factors and immune system deficiencies. Malignant melanoma has been linked to childhood sunburns and sun exposure.
What does malignant melanoma look like?
Melanoma generally begins as a mottled, light brown to black flat blemish with irregular borders. Blemishes are usually at least a quarter of an inch in size and may turn shades of red, blue and white, crust on the surface and bleed. They frequently appear on the upper back, torso, lower legs, head and neck.
A mole that changes in appearance, a new mole or a mole that begins to grow should be examined by a doctor.
When detected early, surgical removal can cure the disease in most cases. Early detection is essential. Dermatologists recommend regular self-examination of the skin to detect changes in appearance, especially changes in existing moles or blemishes. Patients with risk factors should have a complete skin examination annually. Anyone with a changing mole should be examined immediately.
Yes. Because overexposure to ultraviolet light is thought to be a primary cause of malignant melanoma, dermatologists recommend the following precautions:
- Avoid "peak" sunlight hours — 10 a.m. to 3 p.m. — when the sun's rays are most intense.
- Apply a sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of 30 or more.
- Apply sunscreen 15 to 30 minutes before going outdoors so it bonds with your skin and reapply every two hours, especially when playing, gardening, swimming or doing other outdoor activities.
- Wear protective clothing, including a hat with a wide brim and long-sleeved shirts and pants, during prolonged periods in the sun.
UCSF Health medical specialists have reviewed this information. It is for educational purposes only and is not intended to replace the advice of your doctor or other health care provider. We encourage you to discuss any questions or concerns you may have with your provider.







