Liposuction contours and removes fat deposits from areas of the body that don't change with diet and exercise. The most popular form of liposuction as well as the most common cosmetic procedure in the U.S. is tumescent liposuction, which is more effective, safer and less painful than traditional liposuction, and has a quicker recovery time. It is performed as an outpatient procedure and does not require general anesthesia.
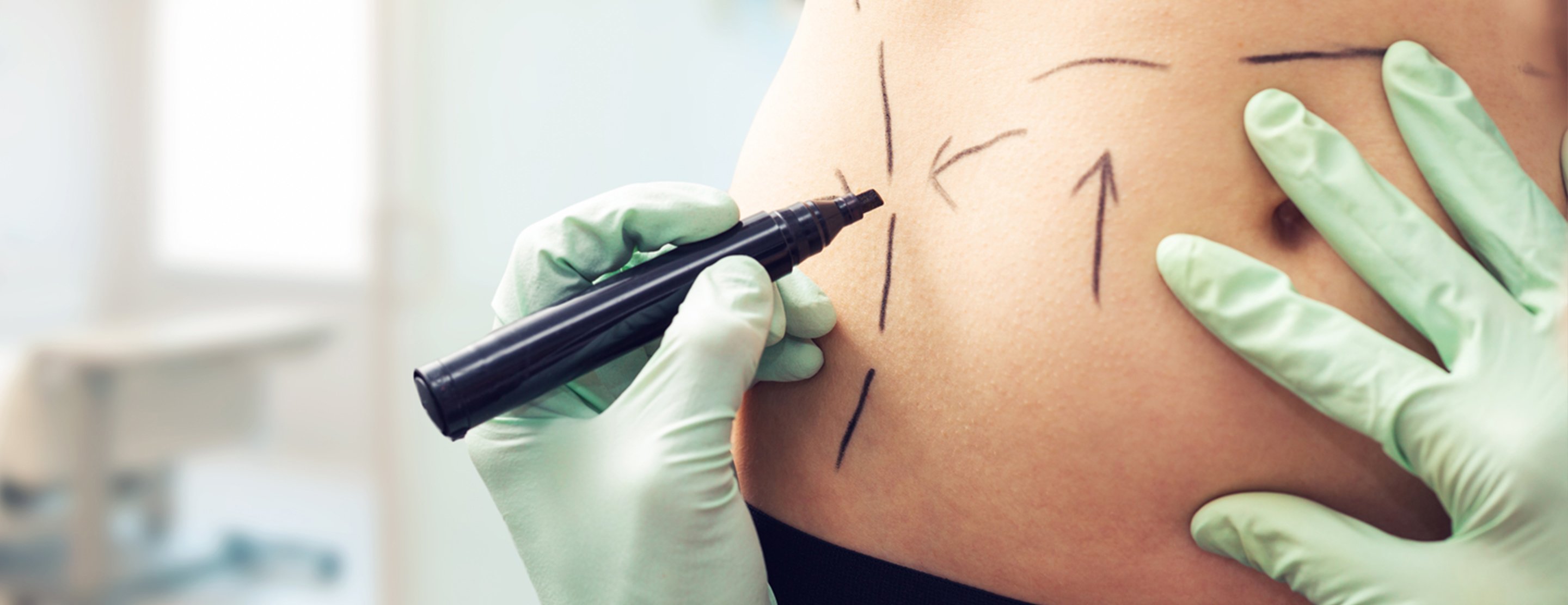
Tumescent Liposuction
Tumescent liposuction can safely remove fat from almost all parts of the body, including the face, neck, chin, breast, stomach, hips, flanks, back, inner and outer thighs, buttocks, knees, calves and ankles. It is used to remove lipomas, or benign fatty tumors, and to treat excessive underarm sweating and enlarged male and female breasts.
Preparation
If you are considering tumescent liposuction, you will meet with a dermatologic or plastic surgeon to discuss your cosmetic goals and determine whether tumescent liposuction is the best approach to meet your needs. Your surgeon will examine your skin and the areas you would like contoured. A complete physical examination will be performed. Photographs will be taken before and after the procedure.
You will discuss your medical history, including previous surgeries, present and past health problems, medications, as well as nutritional and herbal supplements you are taking or have taken at some time.
If you decide to have tumescent liposuction, your doctor will give you specific instructions to follow before surgery. He or she will review medications you regularly take, including nutritional and herbal supplements, and tell you when to stop taking them before surgery.
Other instructions may include:
- If you smoke, stop smoking at least two weeks before surgery, as smoking can hinder wound healing.
- To avoid ingrown hairs, do not shave or remove hair near the areas to be contoured the day of surgery.
- Do not eat or drink anything after midnight the night before surgery. If you need to take medications that have been approved by your doctor, take them with a small sip of water.
- Wear loose-fitting clothing that opens in the front or is easy to remove over your head.
Procedure
A solution containing a local anesthetic and drug called epinephrine will be injected into the targeted areas of excessive fatty deposits. The solution fills the fatty layer of the skin and causes it to swell and become firmer, allowing the surgeon to have better control when contouring the area. The solution also causes the blood vessels to temporarily shrink, greatly reducing blood loss during the procedure, and reduces bruising, swelling and pain after the procedure.
After the solution is injected, the surgeon makes a small incision in the skin and inserts a cannula — a small, skinny tube that is connected to a vacuum-like machine — into the fatty layer. Using back and forth movements, the fat is sucked through the tube into a sterile collection system. An elastic compression garment is then worn to help the skin contract and heal.
Recovery
The local anesthetic injected into the fatty tissue lasts for about 24 hours following surgery. This greatly minimizes postoperative pain. Once this wears off, most patients experience some discomfort that is usually managed with Tylenol.
Most patients are alert and able to function without nausea or grogginess. Walking is encouraged immediately after the procedure to enhance healing. You may resume exercise three to seven days after the procedure. If your job does not involve heavy physical labor, you can probably return to work within a few days.
Most of the swelling goes down in a few days. Although you will see improvement within one to two weeks, it takes at least three to four months, and in some cases as long as six months, to see the treatment's full benefit.
Risks
Like all surgery, tumescent liposuction carries both benefits and risks. Complications are rare and typically minor. The most common include skin irregularity, lumpiness, dimpling, loose skin, numbness, infections and scarring. If these do occur, they can be easily corrected in most cases.
The frequency of complications is significantly reduced when the procedure is performed by a qualified and well-trained dermatologic or plastic surgeon.
UCSF Health medical specialists have reviewed this information. It is for educational purposes only and is not intended to replace the advice of your doctor or other health care provider. We encourage you to discuss any questions or concerns you may have with your provider.