Carotid duplex
Definition
Carotid duplex is an
Alternative Names
Scan - carotid duplex; Carotid ultrasound; Carotid artery ultrasound; Ultrasound - carotid; Vascular ultrasound - carotid; Ultrasound - vascular - carotid; Stroke - carotid duplex; TIA - carotid duplex; Transient ischemic attack - carotid duplex
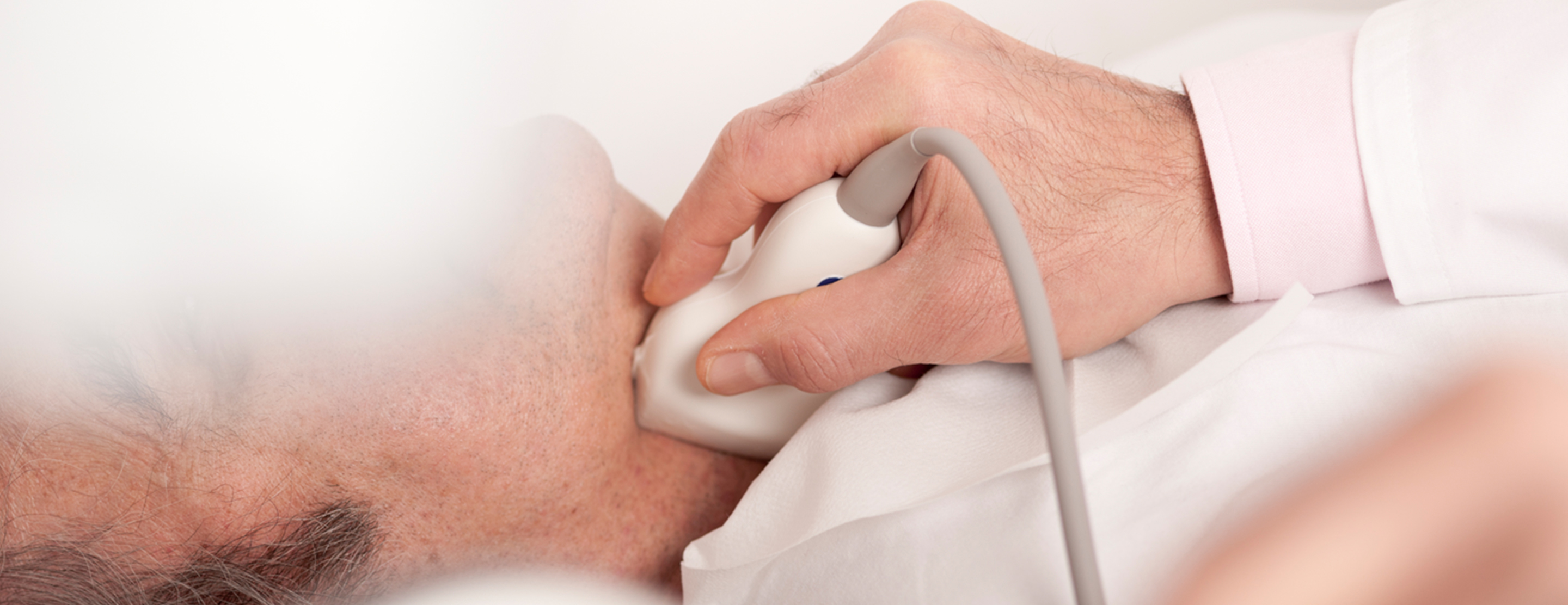
How the Test is Performed
Ultrasound is a painless method that uses sound waves to create images of the inside of the body. The test is done in a vascular lab or radiology department.
The test is done in the following way:
- You lie on your back. Your head is supported to keep it from moving. The ultrasound technician applies a water-based gel to your neck to help with the transmission of the sound waves.
- Next, the technician moves a wand called a transducer back and forth over the area.
- The device sends sound waves to the arteries in your neck. The sound waves bounce off the blood vessels and form images or pictures of the insides of the arteries.
How to Prepare for the Test
No preparation is necessary.
How the Test will Feel
You may feel some pressure as the transducer is moved around your neck. The pressure should not cause any pain. You may also hear a "whooshing" sound. This is normal.
Why the Test is Performed
This test checks blood flow in the carotid arteries. It can detect:
- Blood clotting (thrombosis)
- Narrowing in the arteries (stenosis)
- Other causes of blockage in the carotid arteries
Your doctor may order this test if:
- You have had a
stroke ortransient ischemic attack (TIA) - You need a follow-up test because your carotid artery was found to be narrowed in the past or you have had surgery on the artery
- Your doctor hears an abnormal sound called a bruit over the carotid neck arteries. This may mean the artery is narrowed.
Normal Results
The results will tell your doctor how open or narrowed your carotid arteries are. For example, the arteries may be 10% narrowed, 50% narrowed, or 75% narrowed.
A normal result means there is no problem with the blood flow in the carotid arteries. The artery is free of any significant blockage, narrowing, or other problem.
What Abnormal Results Mean
An abnormal result means the artery may be narrowed, or something is changing the blood flow in the carotid arteries. This is a sign of
In general, the more narrowed the artery is, the higher your risk of stroke.
Depending on the results, your doctor may want you to:
- Consider
surgery - Have additional tests (such as
cerebral angiography , CT angiography, andmagnetic resonance angiography ) - Follow a healthy diet and lifestyle to prevent
hardening of the arteries - Repeat the test again in the future
Risks
There are no risks with having this procedure.
References
Bluth EI, Johnson SI, Troxclair L. The extracranial cerebral vessels. In: Rumack CM, Levine D, eds. Diagnostic Ultrasound. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 26.
Daly C, Rodriguez HE. Carotid artery occlusive disease. Surg Clin N Am. 2013;93(4):813-832. PMID: 23885933
Kaufman JA, Nesbit GM. Carotid and vertebral arteries. In: Kaufman JA, Lee MJ, eds. Vascular and Interventional Radiology: The Requisites. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2014:chap 5.
Review Date: 06/25/2018
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright ©2019 A.D.A.M., Inc., as modified by University of California San Francisco. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
Information developed by A.D.A.M., Inc. regarding tests and test results may not directly correspond with information provided by UCSF Health. Please discuss with your doctor any questions or concerns you may have.





