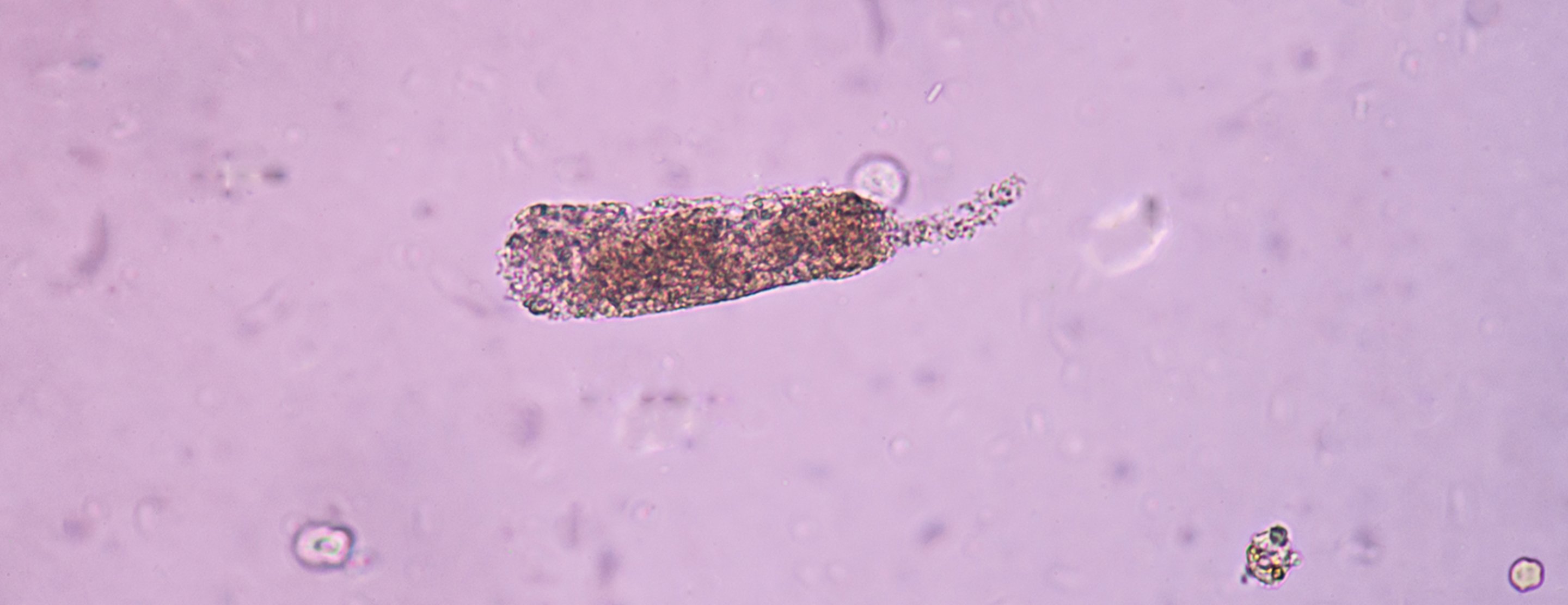
Urinary casts
Definition
Urinary casts are tiny tube-shaped particles that can be found when urine is examined under the microscope during a test called
Urinary casts may be made up of white blood cells, red blood cells, kidney cells, or substances such as protein or fat. The content of a cast can help tell your health care provider whether your kidney is healthy or abnormal.
Alternative Names
Hyaline casts; Granular casts; Renal tubular epithelial casts; Waxy casts; Casts in the urine; Fatty casts; Red blood cell casts; White blood cell casts
How the Test is Performed
The urine sample you provide may need to be from your first morning urine. The sample needs to be taken to the lab within 1 hour.
A
How to Prepare for the Test
No special preparation is needed.
How the Test will Feel
The test involves only normal urination. There is no discomfort.
Why the Test is Performed
Your provider may order this test to see if your kidneys are working properly. It may also be ordered to check for certain conditions, such as:
Glomerular disease Interstitial kidney disease - Kidney infections
Normal Results
The absence of cellular casts or presence of a few hyaline casts is normal.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results may include:
- Fatty casts are seen in people who have lipids in urine. This is most often a complication of
nephrotic syndrome . - Granular casts are a sign of many types of kidney diseases.
- Red blood cell casts mean there is a microscopic amount of bleeding from the kidney. They are seen in many kidney diseases.
- Renal tubular epithelial cell casts reflect damage to tubule cells in the kidney. These casts are seen in conditions such as
renal tubular necrosis , viral disease (such as cytomegalovirus[CMV] nephritis ), and kidneytransplant rejection . - Waxy casts can be found in people with advanced kidney disease and
long-term (chronic) kidney failure . - White blood cell (WBC) casts are common with acute kidney infections and interstitial nephritis.
Your provider will tell you more about your results.
Risks
There are no risks with this test.
References
Judd E, Sanders PW, Agarwal A. Diagnosis and clinical evaluation of acute kidney injury. In: Feehally J, Floege J, Tonelli M, Johnson RJ, eds. Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 68.
Riley RS, McPherson RA. Basic examination of the urine. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 23rd ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2017:chap 28.
Review Date: 07/04/2019
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright ©2019 A.D.A.M., Inc., as modified by University of California San Francisco. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
Information developed by A.D.A.M., Inc. regarding tests and test results may not directly correspond with information provided by UCSF Health. Please discuss with your doctor any questions or concerns you may have.





