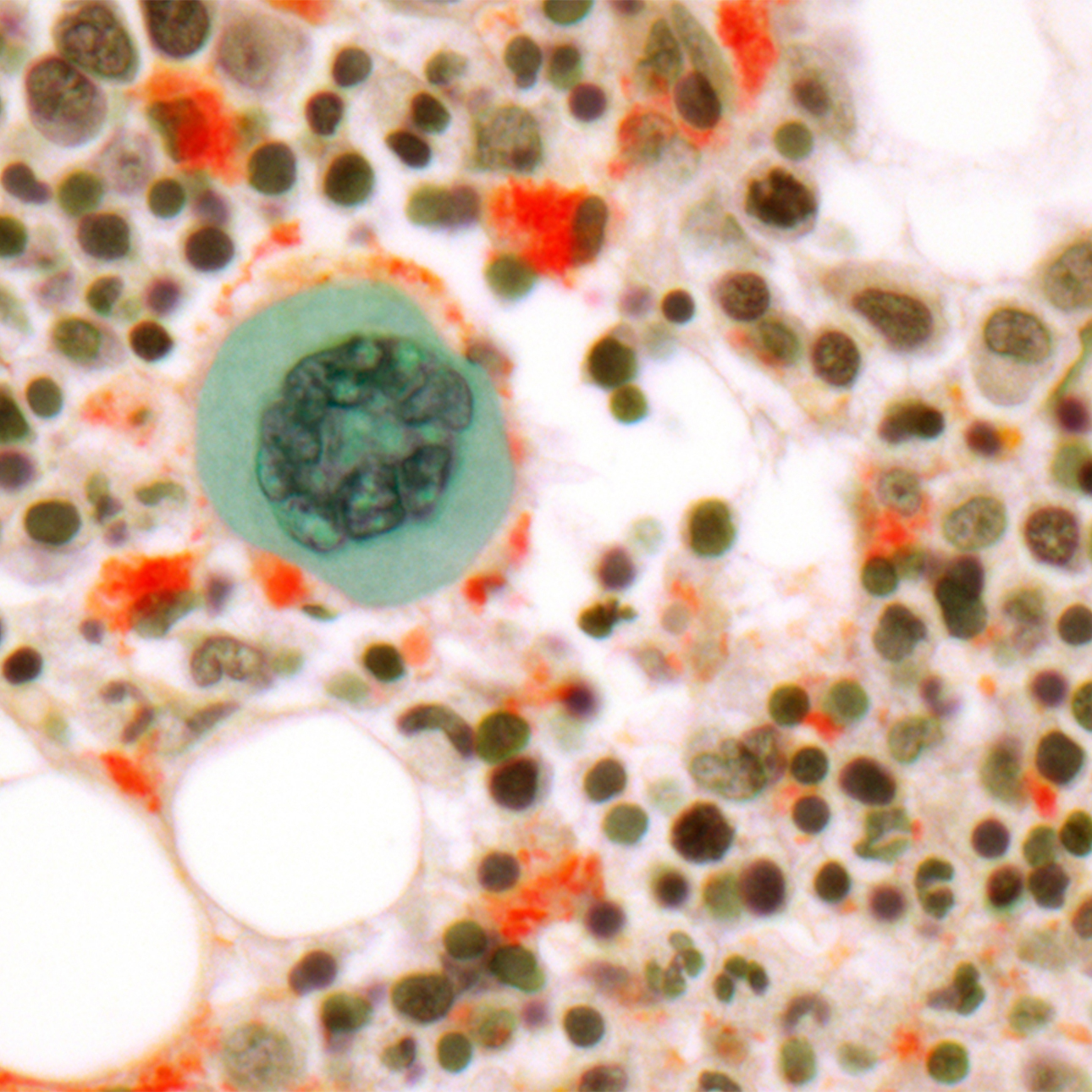
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
Treatments
Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
The mainstay treatment for chronic phase CML is tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), such as imatinib (Gleevec), dasatinib (Sprycel) or nilotinib (Tasigna). TKIs are oral medications that shut down the abnormal protein produced by the BCR/ABL gene.
With TKIs, 80 percent of CML patients will have complete disappearance of the Philadelphia chromosome and restoration of normal blood counts. The life expectancy of chronic phase CML patients taking TKIs has improved from four to six years to well over a decade. In most patients, TKIs prevent conversion to the accelerated or blast phase. Dasatinib or nilotinib works for most patients who are resistant to imatinib.
Side effects of TKIs include rash, upset stomach, swelling of the eyelids, mild lowering of the blood counts and rare episodes of fluid build-up around the lungs and/or heart.
Patients survive a long time with TKIs, but it is still unknown if patients are cured by these drugs. The disease is monitored by a blood test for BCR/ABL every three months, and an annual bone marrow aspiration and biopsy.
Stem Cell Transplantation
The only proven cure for CML is allogeneic blood and marrow transplantation. Before TKIs were available, all chronic phase patients with tissue-matched donors received allogeneic transplantation. Cure rates were 70 to 80 percent. Because of treatment-related mortality of 15 to 20 percent, however, allogeneic transplantation is now reserved for patients failing TKIs.
Investigational Therapies
UCSF is dedicated to improving outcomes of CML patients through the use of investigational therapies and clinical research trials. We currently have new TKIs and related drugs available to treat patients failing the approved TKIs. A world leader in understanding the mechanisms of BCR/ABL resistance to standard TKIs, Dr. Neil Shah, is at UCSF. His laboratory is developing new and better TKIs.
UCSF Health medical specialists have reviewed this information. It is for educational purposes only and is not intended to replace the advice of your doctor or other health care provider. We encourage you to discuss any questions or concerns you may have with your provider.